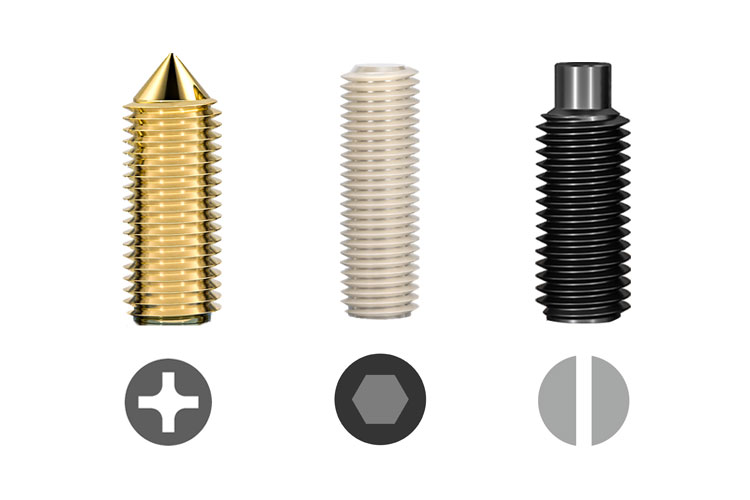

Set screws, also known as flat-head screws, locating screws, stop screws, or headless screws, are threaded fasteners without a traditional head. Their tails come in a variety of designs, including cup point, dog point, cone point, and flat point, and are often made of 8.8/12.9 grade blackened steel or A2/A4 stainless steel.
Set screws are easy to use and function similarly to locating pins, securing two components to prevent axial or rotational movement. They can be installed by inserting a wrench (hex socket, star socket, or flat-head socket) into the slot. Once the set screw is screwed into the part, its end presses against the surface of the other part or fits into the corresponding recess, thereby fixing the relative positions of the two parts.
Specifications for Set Screws
| Diameter range | M1 – M12 (metric) or #0~1/2″ (imperial) |
| Length range | 2mm to 100mm, 1/8″-4″ (customized) |
| Strength class | A2-70, A2-80, A4-70, A4-80; 3.6, 4.6, 4.8, 5.6, 5.8, 6.8, 8.8. 9.8, 10.9, 12.9. |
| Material | Carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, aluminum alloy, nylon, etc. |
| Threads | Coarse thread, fine thread, full thread, half thread. |
| Standard | ISO, DIN, JIS, UNI, BS. |
| Packaging | Plastic bags, plastic boxes, cartons, pallets or customized packaging services |
Surface Finishing
There are various treatment processes for set screws. We cooperate with more than 10 surface treatment manufacturers and can provide any surface treatment service.
| Hot-dip Galvanizing | Black Oxide | Nickel Plating | Phosphating | Polishing | Dacromet |
| Black Zinc Plating | White Zinc Plating | Stainless Steel Passivation | Mechanical Galvanizing | Color Zinc Plating | Chrome Plating |
| Powder Sherardizing | Olive Zinc | Copper Plating | Composite Plating | Electrophoresis | Baking Paint |
| Rustban Coating | Silver Plating | Cadmium Plating | Gold Plating | Zinc-Nickel Alloy | Electroless Nickel |
| Teflon (PTFE) | Atotech | QPQ | Cleaning | Nylok (Nyseal) | Magni Coating |
| Anodizing | Adhesive Coating | Zinc-Aluminum-Magnesium | Blue Zinc Plating | Yellow Zinc Plating | Zinc-Cobalt Alloy |
What Types of Set Screws Are There?
51Fasteners supplies a full range of set screws with various head shapes, such as flat head, cone head, cup head, dog head, square head, and oval head. Drive slots include hexagon socket, cross slot, slotted and torx slot.

Set Screw with Flat Point
Flat point—large contact area, tight fit, does not damage parts, can be used to push hard parts.
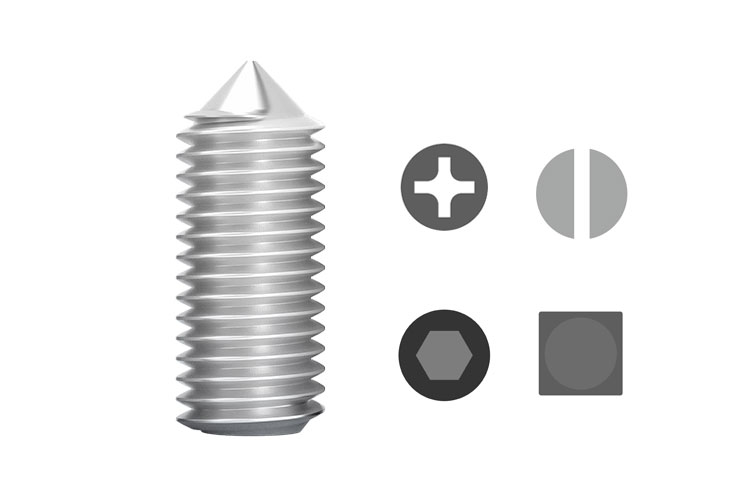
Set Screw with Cone Point
Cone-point screws can use their sharp tips to press tightly against parts and transmit small loads. They are often used in connections that require position adjustment.

Set Screw with Dog Point
Dog point—used in the keyway of the shaft to lock and prevent circumferential rotation, with relatively good results.
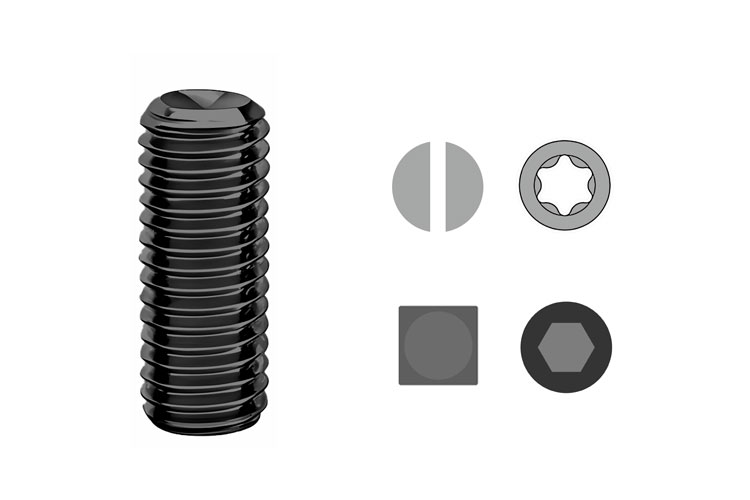

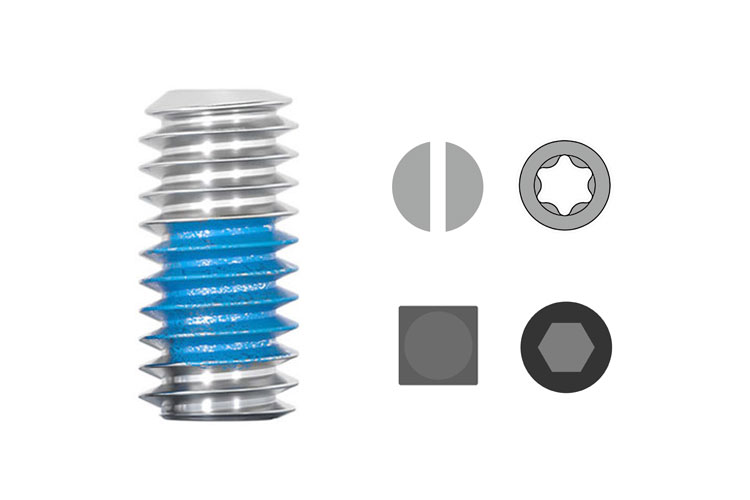
Set Screw with Cup Point
Cup point–more reliable, can withstand greater force, suitable for parts with greater hardness.
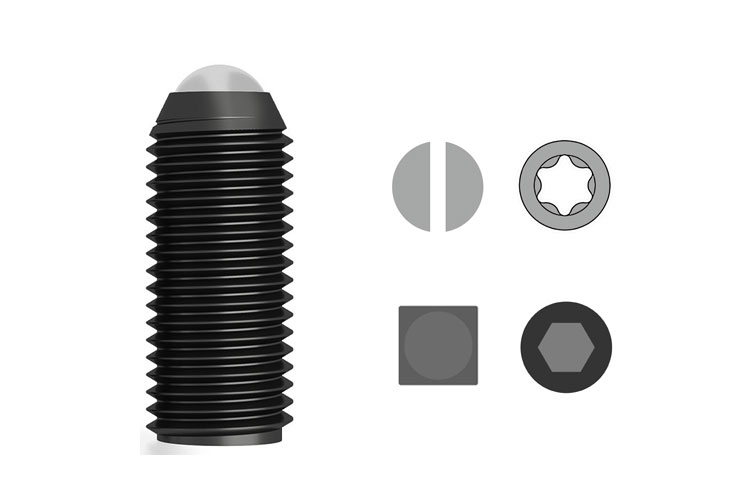

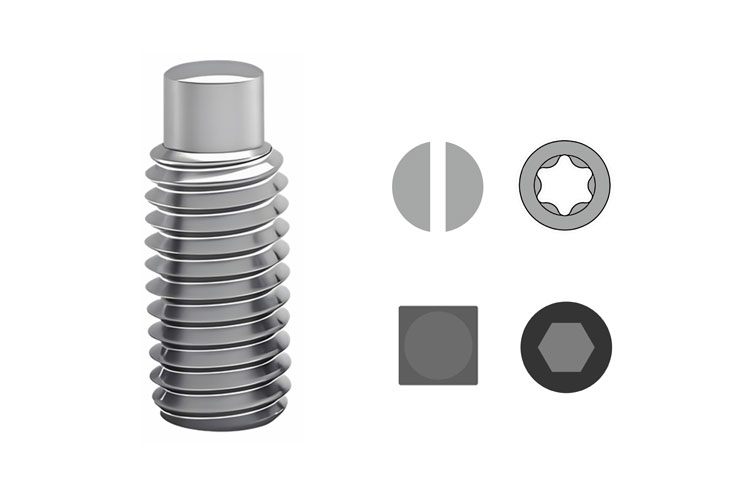
Set Screw with Ball Spring Plunger
By adjusting the spring pressure, the elastic force and preload of the steel ball can be controlled. It is a mechanical component used for precise positioning, clamping, and limiting.
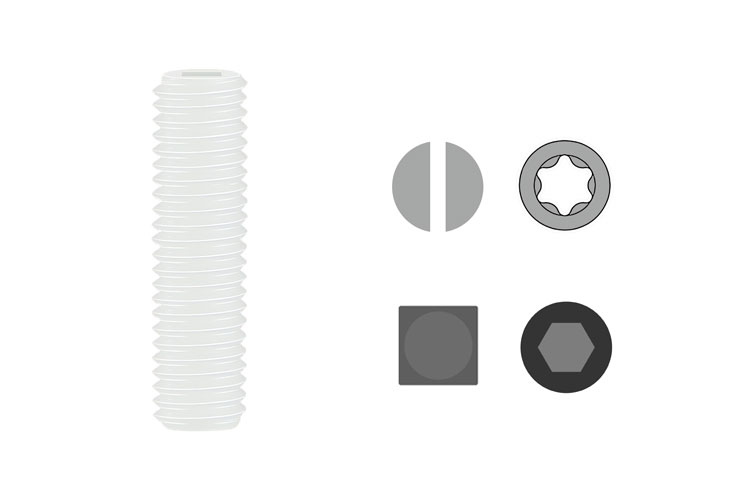
Nylon Set Screw
High-quality nylon eco-friendly material has excellent comprehensive properties, including mechanical properties, heat resistance, insulation, chemical resistance, and flame retardancy.
Standard
| DIN 915 | DIN 34827 | DIN 927 | DIN 914 | DIN 564 | DIN 916 |
| DIN 34827 | DIN 417 | DIN 924 | DIN 926 | DIN 438 | DIN 480 |
| DIN 427 | DIN 479 | DIN 551 | DIN 913 | DIN 922 | DIN 925 |
| DIN 6332 | DIN 553 | ISO 4026 | ISO 4027 | ISO 4028 | ISO 4029 |
| ISO 7434 | ISO 7436 | ISO 4766 | ISO 7435 | ASME B18.6.2 | ASME B18.3.6M |
| JIS B1117 | JIS B1118 | JIS B1177 | EN 27435 | EN 27436 | EN 24766 |
| EN 27434 | BS 2470 | BS4168 | BS 4219 | UNI 5923 | UNI 6050 |
| UNI 5925 | UNI 5927 | ASME B18.3 | NF E25-160 | NF E25-171 | NF E25-161 |
Best One-Stop Supplier of Set Screw Fasteners
We select high-quality materials such as 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel, high-strength carbon steel, nylon, and PEEK plastic to manufacture positioning screws. These materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, high strength, and high toughness.
- Customized production: Production of non-standard set screws according to customer drawings.
- Precision machining: High-precision machining.
- Surface treatment: Various coatings and electroplating.
- Batch production: Supports large orders with timely delivery.
- Quality inspection: Provides material certification and inspection reports.
- Packing: Small Box + Carton +Pallet, Custom Packaging Service.
Application Scenarios
Set screws are widely used in mechanical assembly and precision equipment to fix the relative positions of components and prevent axial or radial displacement.
- Shafts and sleeves: Fixing bearings, gears, pulleys, and other rotating components;
- Electronics: securing PCB boards, heat sinks, or housing structures;
- Molds and fixtures: adjusting and securing mold component positions;
- Automotive and aerospace: engine components, transmission systems;
- Medical devices: endoscopes, surgical instruments, requiring biocompatible materials (such as 316 stainless steel or PEEK).
